Maintaining the quality of printed materials is essential to uphold brand reputation, ensure customer satisfaction, and meet industry standards. Surface inspection systems are instrumental in identifying and rectifying defects, ensuring that printed materials adhere to stringent quality requirements. This article delves into the significance of surface inspection in printed materials, exploring various techniques, advancements in inspection technologies, and their applications across diverse industries.
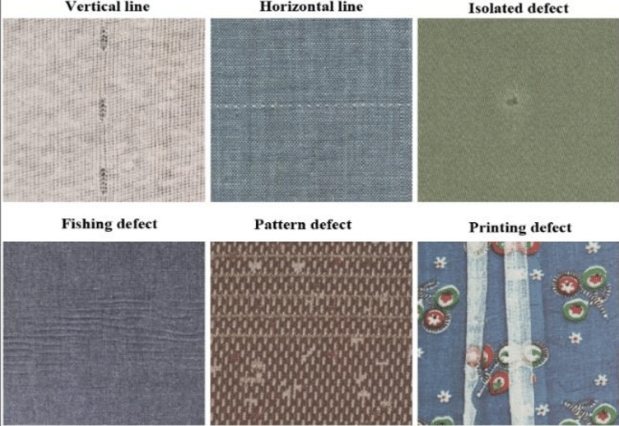
Importance of Surface Inspection in Printed Materials:
Quality Assurance:
Detects and rectifies defects like misprints, color inconsistencies, and registration errors, maintaining high-quality standards crucial for customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Compliance and Consistency:
Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and brand consistency across batches, especially vital in packaging and labeling industries.
Waste Minimization:
Early defect detection minimizes material waste and rework, reducing production downtime and cost overruns associated with remanufacturing.
Preventing Defective Products:
Prevents distribution of defective products, averting customer complaints, returns, and damage to brand reputation.
Optimizing Production Efficiency:
Provides real-time feedback to operators, allowing for immediate adjustments and corrections, thereby optimizing production efficiency.
Ensuring Print Accuracy:
Verifies print accuracy, readability, and alignment, essential for maintaining visual appeal and usability of printed materials.
Security and Authenticity:
Helps ensure authenticity and integrity of printed security features, crucial in security printing applications.
Customer Satisfaction:
Contributes to positive customer experiences by delivering high-quality printed materials that meet or exceed expectations.
Techniques and Technologies Used in Surface Inspection of Printed Materials:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI):
Automated printing quality inspection system utilizes high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms for high-speed defect detection, commonly used in packaging, labels, newspapers, and commercial printing.

Spectrophotometry:
Measures color accuracy and consistency by analyzing spectral characteristics, ensuring compliance with color standards across batches.
3D Surface Profiling:
Employs laser or optical sensors to create detailed three-dimensional maps of printed surfaces, detecting defects such as embossing errors and print thickness variations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
Utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze images and recognize defect patterns, enhancing defect detection accuracy and efficiency.
Real-time Monitoring and Control:
Provides real-time feedback during printing, enabling proactive quality control measures and minimizing production downtime.
Applications of Surface Inspection in Printed Materials:
Packaging Industry:
Quality control, barcodes and labels verification.
Labeling and Branding:
Brand consistency, security features verification.
Publishing and Printing:
Print quality, color consistency verification.
Commercial Printing:
Marketing collaterals, proofing and prototyping.
Security Printing:
Currency and identification documents, secure labels and packaging.
Conclusion:
Surface inspection is indispensable in ensuring the quality and integrity of printed materials across various industries. Advancements in inspection technologies have significantly improved efficiency and accuracy, enabling early defect detection and rectification. By minimizing waste, optimizing production efficiency, and maintaining customer satisfaction, surface inspection systems play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall quality control process in the printing industry.




